Dna Synthesis Can Be Described as
Prokaryotic DNA DNA of prokaryotes and eukaryotes is chemically the same but differs in how it is structurally. A A multi-cellular organism with ACE-2 receptor sites in its cell membrane.
QUESTION 41 Preparation of protein molecules for cellular exportation is the function of which of the following organelles.

. B A cell with a nuclear membrane. Design oligos for your gene of both strands see the notes on primer design below. The key difference between DNA and RNA synthesis is the type of enzyme used for the process.
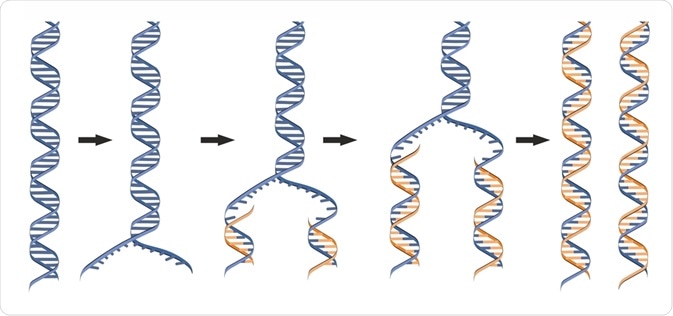
The discovery of the double-helical nature of DNA by Watson Crick explained how genetic information could be duplicated and passed on to succeeding generations. Dilute the oligos to. The throughput of DNA writing ie synthesis is trailing behind with cloning and sequencing constituting the main bottleneck.
Briefly describe the process of dehydration synthesis this can be a definition. Here we show how a new single-molecule PCR smPCR-based procedure can be employed as a. DNA Synthesis Process in Vitro Sometimes there is a need for DNA synthesis outside the living organism in that case in vitro DNA synthesis or replication is needed.
This synthesis can be accomplished using two methods. The application of oxidatively cleavable tritylsulfenyl TrS group to the synthesis of branched DNA is described. The RNA molecules that are copied from these genes which ultimately direct the synthesis of proteins are called messenger RNA mRNA molecules.
It is known to be the process of making a copy of genetic information stored in a DNA strand into a complementary strand of messenger RNA mRNA. The strands of the double helix can separate and serve as templates for the synthesis of daughter strands. DNA and Polypeptide Synthesis DNA in prokaryotes and eukaryotes The genetic code is universal- the same nucleotide base-pairing code is used in all living organisms both prokaryotes and eukaryotes to instruct protein synthesis.
D A cell that has only RNA lacking DNA. Results Synthesis of Leading and Lagging Strands. The strands of the double helix can separate and serve as templates for the synthesis of daughter strands.
DNA synthesis or replication is described as semiconservative because each DNA molecule is made up of one old and one new one. What does anti-parallel mean AND why is it necessary for DNA to line up in this way. DTS can generate products unrelated in structure to the DNA backbone in a sequence-specific manner.
A synthetic minicircle template with a replication fork has recently been described that can be used to examine the synthesis of leading and lagging strands during rolling circle replication ref. The synthesis process is also very useful in various genetics. The new platform for DNA data storage combines four chips and can.
DNA synthesis by DNA polymerases always proceeds in the 53 direction using a complementary antiparallel strand as template. C A cell with no nuclear membrane. DNA synthesis is the process of synthesizing a double stranded DNA through semi-conservative replication by using enzymes.
While both protocols are similar they have some distinct differences which will be described here. An enzyme polymerase catalyzes the synthesis reaction. We previously described the generality of DNA-templated organic synthesis DTS and explored its potential for translating DNA sequences into corresponding synthetic products by using DNA hybridization to modulate the effective molarity of DNA-linked reactants.
The process of making new deoxyribose nucleic acid DNA is known as DNA synthesis. To overcome this bottleneck an in vitro alternative for in vivo DNA cloning needs to be integrated into DNA synthesis methods. The majority of genes carried in a cells DNA specify the amino acid sequence of proteins.
Up to 24 cash back 5. QUESTION 40 Transcription can be best described as the. A Eukaryote can be described as.
The current chemical synthesis of DNA fragments requiresmultistepproceduresfortheintroduc-. The TrS protecting group can be removed by treatment with 1 M aqueous iodine while it is stable toward an oxaziridine-type oxidant. DNA is a polymer consisting of repeating units known as A dipeptides C amino acids B nucleotides D organic salts Watson and Crick described the DNA molecule as a B single strand A straight chain D branching chain C double helix The diagram below represents the building block of a large molecule known as a C protein carbohydrate.
The secondary structure of a double-stranded DNA helix molecule can best be described as a _____. At the Built With Biology Conference formerly known as SynbioBeta GenScript Innovation Center VP Cedric Wu described the firms new semiconductor technology the High-Density DNA Synthesis Chip which can synthesize approximately 84 million unique oligos up to 170 bases long. Providing room for an RNA primer so that lagging strand synthesis can be completed to the end of the chromosome.
In conservative replication the two daughter strands would go to one daughter cell and. A b c d synthesis of DNA. Transcription can best be described as the.
Quiz 3 - ANSWER KEYdocx - BIOL 1001 Quiz 3 Fall 2017 Name_ 1. DNA is often described as aligning anti-parallel. The discovery of the double-helical nature of DNA by Watson Crick explained how genetic information could be duplicated and passed on to succeeding generations.
Which is an example of. At the same time the sulfur-oxygen linkage showed sufficient stability under the acidic and basic conditions used in. As described in the central dogma of biology information from a gene can be used to build a protein in a two-step process.
Transcription is considered to be the first step of gene expression. Process Importance and Direction. DNA Synthesis Without Base Protection UNIT 310 An ultimate goal in the chemical synthesis of DNA is the ability to form O-selective in-ternucleotide bonds without the use of base-protecting groups as can be done by enzy-matic synthesis using DNA polymerases.
DNA synthesis is a natural process found in all organisms and we know it as replication. Ligase Chain Reaction LCR or Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR. RNA synthesis is the process of synthesizing an RNA through the process of transcription using an enzyme-mediated method.
Reading of mRNA codons by tRNA. In conservative replication the two daughter strands would go. The template offers several experimental advantages.
The final product of a minority of genes however is the RNA itself.

Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
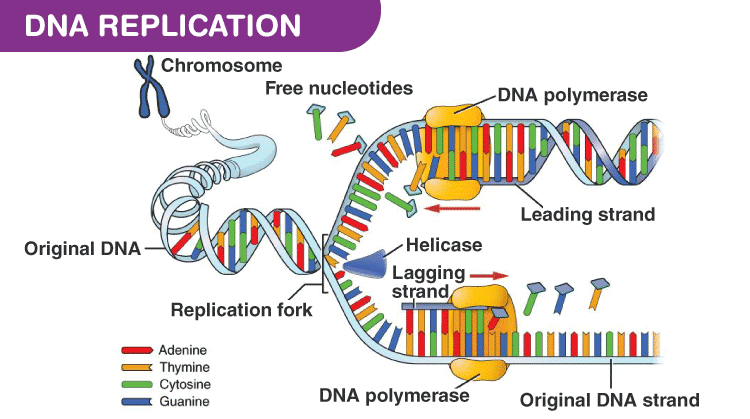
Dna Replication Steps Rules Dna Polymerase Enzymes Rna Primer Synthesis Science Online

Dna Replication S Phase Checkpoint Control Learn Science At Scitable

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Replication Checkpoint Dna Synthesis Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Synthesis Google Search Dna Replication Dna Research Science Biology

Extensive Coevolution In Dna Replication Genes Cartoon Representation Download Scientific Diagram

Steps Of Dna Replication Dna Polymerase Dna Replication Science Notes
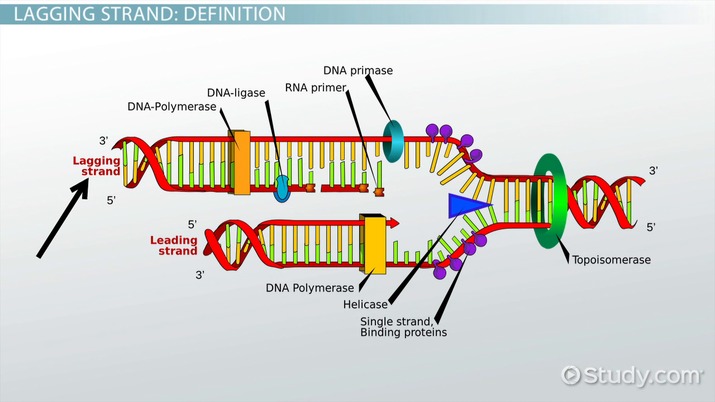
Lagging Strand Synthesis In Dna Replication What Is The Lagging Strand Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication

Dna Synthesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
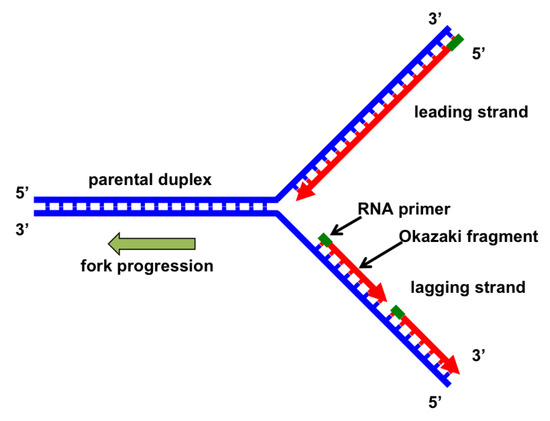
Genes Free Full Text The Replication Fork Understanding The Eukaryotic Replication Machinery And The Challenges To Genome Duplication Html

Dna Replication Checkpoint Dna Synthesis Learn Science At Scitable
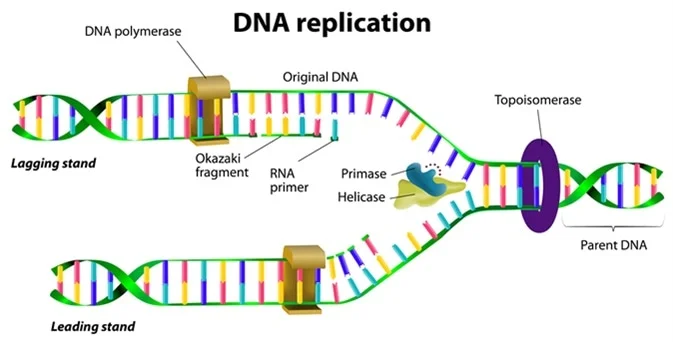

Comments
Post a Comment